In actual deployment of wireless APs, different installation locations may result in different WiFi effects. So how to find the best location is crucial. The following uses a simple example to compare the WiFi coverage effect of wireless APs in different locations and experience the guiding principles of AP installation.
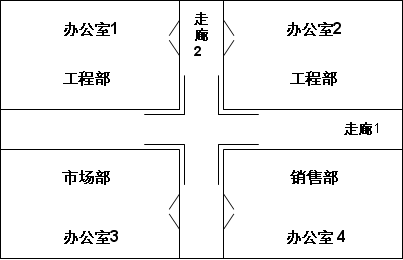
When deploying a wireless network, the surveyed scenes are as shown in the figure. If you use the RD-W68AP to build:
Environmental features:
1. The two crisscross corridors are divided into four offices and separate three different departments.
2, the engineering department will often have a large number of users, they have higher requirements for bandwidth.
3, The marketing department and the sales department office staff are few, they do not require high bandwidth, but the two departments often move between each other.
4. The location of each room near the intersection of two corridors is the load-bearing wall. At the same time, many handicrafts are also placed outside the corridor. This area attenuates RF signals greatly.
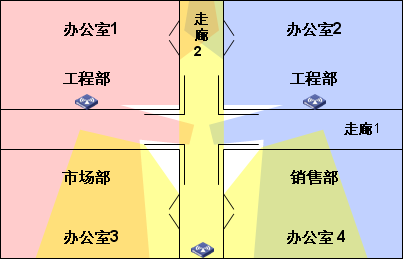
Deployment Design 1:
Due to the large number of users in the engineering department and the high bandwidth requirements, each office has an RD-W68AP wall mounted on the wall.
The walls of the two RD-W68AP installation positions of the engineering department are ordinary partition walls, and the signal loss is small. Therefore, most of the market and sales departments can also be covered by the signals of these two RD-W68APs. Deploy the 3rd RD-W68AP between the marketing department and sales office to solve the problem of blind coverage of signal coverage.
The problems exposed by the above deployment scenarios are:
1, there is no comprehensive consideration from the user applications, user density, workflow and other aspects.
2. There are signal coverage blind areas in some areas.
3. In the office areas of the marketing department and the sales department that need frequent movements, switching between different signal coverage areas occurs when the user moves.
4. Users moving in corridor 1 can only be covered by leaked signals, and the signal quality is poor.
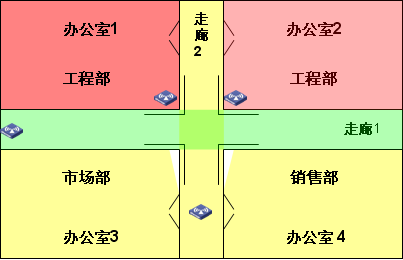
Deployment Design Option 2:
Due to the large number of users in the engineering department and the high requirement for bandwidth, each office is equipped with an RD-W68AP, while the RD-W68AP installation position is moved to the corner of the bearing wall and a directional flat antenna is used to cover the respective offices. This will ensure that each RD-W68AP signal is concentrated in its own room, while using the weight loss of the bearing wall to prevent the signal from leaking out of the room.
The RD-W68AP between the marketing department and the sales department is placed at the door of the two offices so that one RD-W68AP can cover the two office areas. Wireless users in the mobile office will no longer experience handover across small areas. . A high-gain directional antenna is used to cover the corridor 1 at one end of the corridor 1.
From the comparison of Scenario 1 and Scenario 2, it can be seen that Scenario 2 is obviously more in line with the principle of “signal coverage is more in line with the scenario scope and service requirements of the target coverage area†while minimizing the visibility between spatial signals.
1,2-Epoxybutane
1,2-Epoxybutane is a colorless liquid with a sweet odor. It is also known as butylene oxide and is used in the production of various chemicals, including glycols, glycol ethers, and polyurethanes. It is a highly reactive compound and can cause skin and eye irritation, as well as respiratory problems if inhaled. It is also considered a potential carcinogen and should be handled with care.