The moisture in the solid bulk material can be divided into the following types according to its distribution characteristics:
Gutter Downspout Roll Forming Machine
Gutter Downspout Roll Forming Machine is the special equipment for continuous rolling and cold-forming on steel sheet. It adopts coiling steel sheet as the raw material, decoiling the coil, continuous rolling and cold-forming, automatically cut to the size and output the finished panel. The equipment adopts PLC control, AC frequency and adjusting the speed technology, and it realizes the continuous automatically production, therefore, it is really a new type of energy-saving and high-effective producing equipment for steel structure.
Main parameters of rain water gutter roll forming machine
Suitable to process: Color steel plate, galvanized sheet, aluminum coils,etc.
Width of the feeding material:According to the profile.
Rollers station: 18 rows.
Thickness of feeding material:0.3-0.8mm
Power:4+4kw
Size:8500*800*1500mm
Productivity: 8-12m/min
Diameter of shaft: 60mm
Weight: About 4.8 Tons
Voltage: 380V 50Hz 3phases
Roller material:Carbon Steel 45#
Material of the cutting : Cr12
Wall thickness of main forming machine: 16mm steel plate
Main frame of the machine:300 H steel
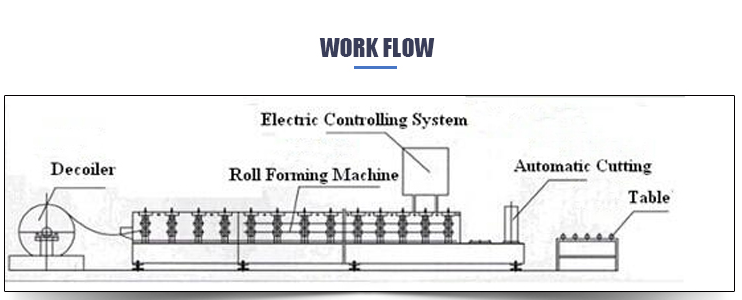
Components of line
1.Decoiler 1 unit
2.Roll Forming System 1 unit
3.Cutting Device 1 unit
4.Hydraulic Station 1 unit
5.PLC control system 1 unit
Working Flow:
Loading coil – decoiling – guide feeding – main roll forming – PLC system - hydrarlic cutting – finished products
Gutter Downspout Roll Forming Machine Gutter Downspout Roll Forming Machine,Gutter Roll Forming Machine,Steel Downspout Roll Forming Machine,Rain Gutter Roll Forming Machine CANGZHOU DIXIN ROLL FORMING MACHINE CO., LTD , https://www.hebeimachine.com
1. Gravity moisture The moisture stored in the gap between solid particles is called gravity water. Gravity water can flow freely under the action of gravity, and there is no interaction force between the materials and the material. It is only restricted by the container and is the most easily removed water in the material.
2. Capillary Moisture Due to the existence of many fine pores between the loose materials, sometimes there are holes or cracks inside the solid particles, and many of these pores can produce a capillary action. The moisture retained by these capillary forces by capillary forces is called capillary moisture.
Tests have shown that the smaller the particle size of the material, the higher the capillary moisture content, but when the particle size is small to a certain value, the increase in water content is small. This is because the particle size is small, and the gap in which moisture can be accommodated is also small. It is difficult to remove capillary water. Forced filtration is used, that is, pressure or centrifugal force is used to separate moisture from the solid particles.
3. Film moisture The layer of hydrated film bound to the surface of solid particles due to the dipole action of water molecules is called film moisture. This is a water that is difficult to remove, and it is difficult to remove it even with strong centrifugal force, and it can only be removed by drying.
4. Moisture absorption due to the adsorption of solid particles on the surface of the particles, the water molecules are adsorbed on its surface, and through the osmosis to reach the interior of the solid particles itself, the moisture attached to the surface of the particles is called moisture; the water that penetrates into the particles Called to absorb moisture. These two kinds of water are combined to be called hygroscopic water. This is the most difficult to remove moisture, even if it is heated by heat, it cannot be completely removed. If it is placed in a humid air, it will re-absorb.
Therefore, in determining the process of dewatering the material and the water content that may be achieved, the distribution characteristics of the moisture of the material should first be ascertained.