The fixing angle of a Tower Crane refers to the angle at which the crane is secured to its base or foundation. It is important to ensure that the crane is properly fixed at the correct angle to ensure stability and safety during operation.
It is important to follow the manufacturer's guidelines and recommendations when setting the fixing angle of a tower crane to ensure safe and efficient operation. Improper fixing angle can lead to instability, tipping, or other safety hazards.
Tower crane fixing angle is connected between tower body and concrete foundation. Usually, the model of fixing angle is based on the tower crane Mast Section, such as 1.2m s24 mast section, 1.6m L46a1 mast section, 2.0m l68b2 mast section.
Fixing angle is used for connecting of tower crane foundation and tower crane body. Usually the fixing angle is fixed inside the concrete foundation. However, there is one type of tower crane fixing angle which is reusable type. The reusable type fixing angle could be removed from the foundation after tower crane disassembly. Fixed Leg Fixing Angle,Reusable Fixing Angle,Tower Crane Fixing Angle,Tower Crane Reusable Fixing Angle,Foundation Anchor Fixing Angle SHEN YANG BAOQUAN BUSINESS CO., LTD , https://www.sczenghui.com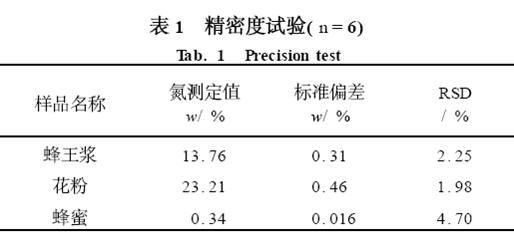


The fixing angle of a tower crane is typically determined by the manufacturer and specified in the crane's operating manual. It is usually set at a specific angle to provide optimal stability and load capacity for the crane.
The fixing angle can be adjusted during the initial installation of the crane to ensure it is level and properly aligned. This is typically done using leveling jacks or other adjustable components at the base of the crane.

Improvement of Protein Determination Method in Bee Products
The determination of protein in bee products mainly uses the Kjeldahl method, which is stable and reliable and widely used. However, the operation is complicated and the digestion time is long. It requires distillation and titration, which takes time and effort. This method improves the digestive conditions by using hydrogen peroxide 2 concentrated sulfuric acid mixture as the digestive liquid and during the digestion process, nitric acid 2 perchloric acid mixed acid is added dropwise to shorten the digestion time. The protein in the sample is decomposed by heating together with sulfuric acid and a catalyst. The resulting ammonia reacts with the sulfuric acid to produce ammonium sulfate. The ammonium sulfate produces hypochlorite in alkaline solution to form monochloramine, which is catalyzed by sodium nitroferroyanide. Blue compounds with salicylic acid can be colorimetrically quantified at 655 nm.
1 Test section
1. 1 Instruments and reagents
Nitrogen determination instrument; visible spectrophotometer. Coloring agent: Weigh 5 g of salicylic acid, add water 20 mL, add 2 mol · L - 1 sodium hydroxide solution 16 mL, Kjeldahl instrument; stirring to completely dissolve, and then take 5. 0 g Potassium sodium tartrate was dissolved in a small amount of water and the above solutions were combined and transferred to a 100 mL volumetric flask and diluted with water. Sodium hypochlorite solution: The calibrated solution of sodium hypochlorite was diluted with sodium hydroxide solution to a concentration of 3. 5 g.L -1 containing available chlorine, and the free base concentration was 0. 75 mol.L -1 (calculated as sodium hydroxide). . Nitroferronitrile sodium solution: Weigh nitrosferricyanide sodium (sodium nitroprusside) 1. 0 g, dissolved in a small amount of pure water, and diluted to 100 mL with a mass concentration of 10 g.L-1. Ammonia nitrogen standard solution: Diluted to a standard working solution with a concentration of 1. 0 mg ・L -1 ammonia nitrogen when in use. All reagents are analytically pure, and water is ammonia-free deionized water.
1. 2 test methods
1. 2. 1 Sample processing
Weigh the sample 2. 0 g in a 250 mL nitrocellulose bottle, add 0.5 g of copper sulfate, 5.0 g of potassium sulfate, and 20 mL of sulfuric acid 2 hydrogen peroxide (2 + 1) mixture; Put a small funnel on the mouth and place it on an adjustable electric furnace with asbestos mesh. Heat a small fire until the foam stops. Increase the firepower and slowly add nitric acid 2 perchloric acid (4 + 1) Mixed acid 2 - 3 After the sample solution is bluish and transparent, continue heating for 30 min. After removing cooling, add 20 mL of water. Cool and wash in 500 mL (250 mL of honey dilute solution) in volumetric flasks. Pipette 5.0 mL of the sample digestion solution into another 100 mL volumetric flask, add water to the scale, and use as a reagent blank.
1. 2. 2 Sample Analysis
2. To remove sample solution and reagent blank solution 2. 0~5. 0 mL, 1. 0 mg ・L - 1 ammonia nitrogen standard working solution 0, 0. 50, 1. 00, 2. 00, 4. 00, 6. 00 , 8. 00 mL, respectively, in 10 mL plug colorimetric tube, to the sample tube, reagent blank tube and standard tube plus color reagent 1. 0 mL, 10 g · L - 1 Nitro ferricyanide solution 0. 2 mL, 3. 5 g ・L - 1 hypochlorite solution 0.2 mL, dilute with water to the mark, mix, stand for 60 min, and measure at a wavelength of 655 nm with a 1.0 cm cuvette The absorbance, draw a standard curve, calculate the protein content of the sample solution.
2 Results and Discussion
2. 1 working curve
According to the test method for the determination of the standard series solution, the nitrogen concentration in the range of 0 ~ 0. 8 mg · L - 1 was linear, and the reagent blank was measured 20 times. The standard deviation of 3 times was the detection limit. The detection limit was 0. 014 mg · kg - 1 .
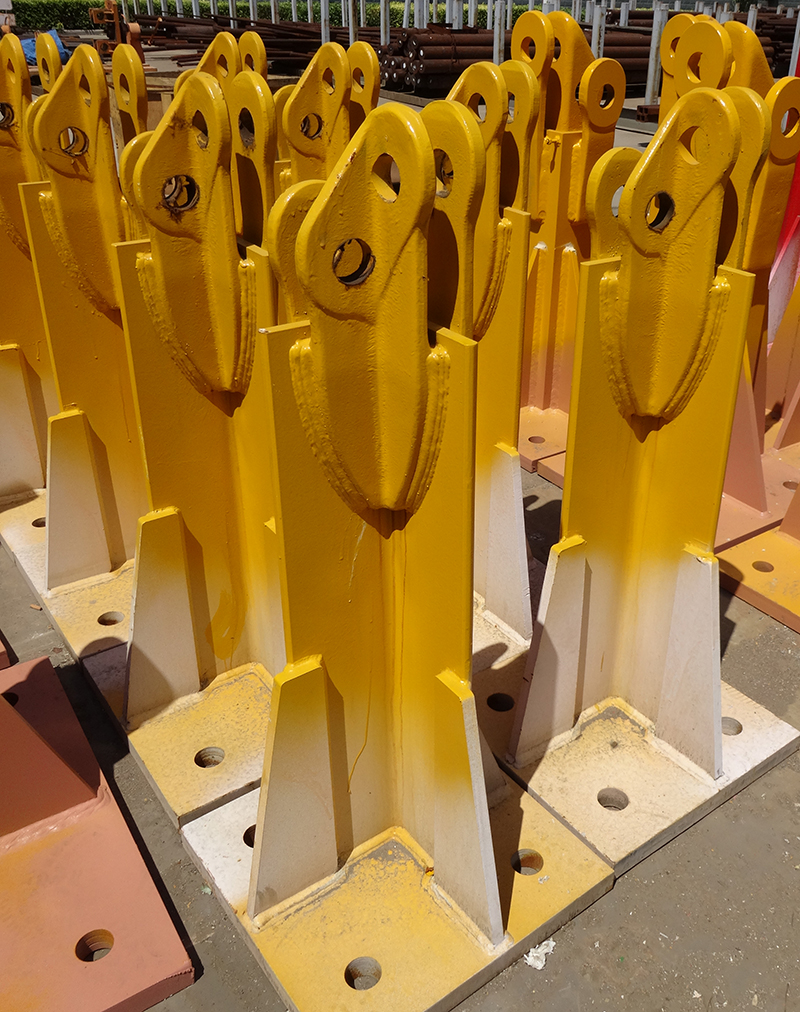
2. 2 precision test
The samples of royal jelly, pollen and honey were taken and tested six times according to the test method. The results of the relative standard deviation (RSD) of the measured values ​​of the samples are shown in Table 1.
2.3 Comparison of the determination results of salicylic acid method and Kjeldahl nitrogen distillation method
Eight samples of peak products were randomly selected and the protein in the samples was determined by the salicylic acid method and the Kjeldahl nitrogen distillation method. The results were analyzed by t-test, t = 0. 153, and the t-value table was examined. 7) = 2.356,
Therefore, P > 0.05. There was no significant difference between the two methods in the determination of protein in bee products. The results are shown in Table 2.
2.4 Recovery Test
Take royal jelly, pollen, bee dense sample, add ammonia nitrogen standard solution, according to the test method for sample processing and determination, the determination results of recovery rate are shown in Table 3.
By improving the conditions for protein digestion of bee products, the reaction time was effectively shortened from the original 3.5 h to about 2 h. As the salicylic acid photometric sample digestion solution does not require distillation, it is directly used for determination and is more suitable for the determination of batch samples. There is no significant difference between salicylic acid photometry and national standard method, so salicylic acid photometry is easy to operate. Accurate and rapid, it can be used for the determination of protein in bee products.