For the term "cloud computing", everyone has already been familiar with it. But for many new "whites", the various concepts involved may be unfounded. This article is from the most basic point of view and hopes to be your quick start manual.
Concept
In 2006, Google CEO Eric first proposed the concept of "cloud computing" at the search engine conference. In the past two years, it has been gradually commercialized by companies such as Amazon, Ali, and Microsoft.
To put it simply, cloud computing is the centralized deployment and redistribution of computer hardware, systems, networks, application software and other resources in order to maximize the utilization efficiency of computing resources. The initial goal of cloud computing is to manage resources. The main management areas are computing resources, network resources and storage resources.
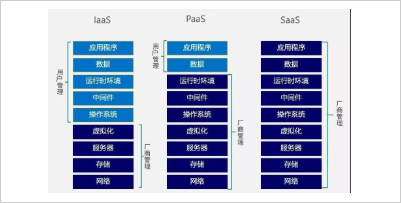
Specifically, cloud computing includes a three-tier architecture: IaaS, SaaS, and PaaS.
1.IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
The services that IaaS provides to customers are the use of infrastructure for all computers, including virtual machines, processors (CPUs), memory, firewalls, network bandwidth, and other basic computer resources.
The usage fee for this service can be calculated on a number of criteria, such as hourly cost per processor, data stored per hour (GB), network bandwidth used, and growth services used.
To be a pioneer in the field of IaaS, non-Amazon, and of course some leading providers such as Rackspacem, Gogrid, Joyent, etc.
2. SaaS (Software as a Service)
The service SaaS provides to users is an application that can run on the "cloud." That is to say, users can connect applications in the "cloud" on various devices, users do not need to manage or control any cloud computing facilities, such as servers, operating systems and storage.
The most common SaaS are collaboration applications such as Google Apps; online project management applications, customer relationship management with salesforce.com and Microsoft Dynamics, and cloud-based storage and sharing services such as Dropbox and Skydrive.
Here is a quiet reminder that SaaS is ideal if you want to focus on the main business, instead of wasting time hiring and retaining IT staff.
3. PaaS (platform as a service)
Paas means that the entire life cycle of the software is done on PaaS. This service is designed for developers, testers, deployers, and administrators of applications.
Common PaaS are: GAE preferred by Java and Python developers; WindowsAzure for enterprise users; Java users choose Amazon's Beanstalk.
If these three architectures are not understood, it does not matter, the business model of cloud computing is easier to understand, and can be roughly divided into three categories: public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud.
1. Public Cloud
Public cloud is a service that provides computing resources to the public. It is owned, managed, and operated by commercial organizations, academic institutions, or government agencies, and public clouds are deployed within the service provider's premises. Users use cloud services over the Internet, paying for usage or by ordering.
The advantage of public cloud is low cost and very good scalability. The disadvantages are lack of control over cloud resources, security of confidential data, network performance and matching issues. Public cloud service providers include Amazon, Google, and Microsoft.
2. Private Cloud (Private Cloud)
In the private cloud model, the resources of the cloud platform are dedicated to a single organization that contains multiple users. A private cloud can be jointly owned, managed, and operated by the organization, a third party, or both. The deployment location of the private cloud can be internal to the organization or external. Private cloud service providers are primarily IBM and Amazon.
Let's take a look at two implementations of private clouds:
Internal (on-premise) private cloud:
Also known as an internal cloud, it is built by organizations in their own data centers. This form has limitations in scale and resource scalability, but it is conducive to standardizing cloud service management processes and security. Organizations still have to bear the cost of capital and maintenance costs for physical resources.
This approach is suitable for organizations that require complete control over applications, platform configurations, and security mechanisms.
External (off-premise) private cloud:
This private cloud is deployed outside the organization and is managed by a third-party agency. Third parties provide a dedicated cloud environment for the organization and guarantee privacy and confidentiality. The solution is less costly than the internal private cloud and is also easier to scale up.
3. Hybrid Cloud
In the hybrid cloud model, the cloud platform is a combination of two different modes (private or public) cloud platforms. These platforms are still separate entities, but they are bundled using standardization or proprietary technology, enabling the migration of data and applications between each other.
With the hybrid cloud model, an organization can deploy secondary applications and data to the public cloud, leveraging the scalability and cost advantages of the public cloud. At the same time, mission-critical applications and data are placed in a private cloud for greater security.
Hybrid cloud service providers are primarily IBM and Microsoft.
With the development of cloud computing, pure public or private clouds have been difficult to meet the needs of existing businesses. Hybrid cloud and cloud have become new solutions to problems. IDC predicts that the global future hybrid cloud will occupy the entire cloud market share. 67%.
Market articles
Recently, the cloud computing industry report was released in the third quarter of 2018. The report pointed out that as the global cloud computing market continues to grow, the concentration of the industry will further increase, and more and more cloud spending will flow to a few head cloud computing companies such as Amazon, Microsoft and Alibaba.
Head-ends such as Amazon, Microsoft, and Alibaba account for more than 55% of the core cloud computing market, and this number is still rising rapidly. Goldman Sachs expects that their combined market share will reach 84% by 2019.
Market research firm Gartner also released the "2018 IaaS Magic Quadrant" report, in which only six cloud service providers were shortlisted, compared with 15 cloud service providers in 2017, 60% of manufacturers disappeared from the list.
The development of the cloud computing market towards the oligopoly has become more and more an industry consensus. Cloud computing After more than 10 years of vendor chaos, the giants gradually began to dominate the market.
Summary <br>
Previously, China's cloud market was in a wait-and-see stage, and in 2018 it was a transition period between the cloud and the vertical industries. Regardless of policy supervision or customer recognition, it has shown great benefits for the promotion of enterprises on the cloud.
However, is there really a lot of opportunity left for us? Especially for small and medium-sized enterprises, it is not easy to split a big cake on the cloud market.
At present, the market structure has been basically determined. The head manufacturers represented by Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, Alibaba Cloud and Google Cloud will gradually monopolize most of the market share, while small and medium-sized manufacturers can only obtain a partial share in the market segment. And facing the further squeeze of the head manufacturers.
GMM1200 Double Side Surface Grinding Machine
High precision double side surface grinding or fine grinding is a super finishing process performed by removing material from two surfaces of a component resulting in extremely precise geometric accuracy and surface finish. Typically, it is the last grinding step of a mechanical production chain utilized to improve and/or correct the geometry of parts coming from sintering, sawing, molding or similar operations. Depending on the application, the stock removal also can be taken from just one surface.


