A hydraulic shearing machine is a powerful tool used in various industrial applications to cut sheet metal and other materials with precision and efficiency. This machine uses a hydraulic system to exert force on the blades, enabling precise and clean cuts. Hydraulic shearing machines have a rich history dating back to the mid-20th century. The concept was first invented in 1949, but it wasn't until the late 1960s that these machines began to gain widespread adoption in the metalworking industry. The early models, such as the Scotchman 314, were built to last, with many still operational today, showcasing the durability and reliability that has become synonymous with hydraulic shearing technology. Hydraulic shearing machines have become indispensable tools in modern metalworking and fabrication. Their versatility, precision, and efficiency make them crucial in various industries, including metal fabrication, automotive manufacturing, aerospace production, construction and structural steel fabrication, shipbuilding, electronics, and electrical appliance manufacturing. These machines play a vital role in cutting metal sheets, plates, and bars with high precision, contributing significantly to the production of components used in a wide range of products and structures. Their ability to handle different materials and thicknesses while maintaining accuracy has made them a cornerstone of efficient manufacturing processes. This article provides a comprehensive overview of hydraulic shearing machines, detailing their key components, working principles, and different types. Additionally, it explores the benefits of hydraulic shearing machines, and their widespread applications. The frame is the backbone of the hydraulic shearing machine, providing the necessary structural support. It includes left and right racks, beams, and a guide table, all bolted together to form a rigid and stable assembly. Typically constructed from robust steel, the frame maintains the alignment and stability of other components, ensuring accurate and consistent cutting operations. It houses various elements like the hydraulic system, blades, and controls. The hydraulic system is the powerhouse of the shearing machine, driving the movement of the shearing blades. It consists of several key components: The hydraulic pump generates the necessary pressure in the hydraulic fluid. This pressure drives the entire system, enabling the controlled motion of the blades. Hydraulic fluid transmits force throughout the system. It must be maintained at optimal levels and purity to ensure efficient operation and prevent wear. Hydraulic cylinders are responsible for moving the upper shearing blade up and down. They convert hydraulic energy into mechanical motion. Valves and lines control the flow and pressure of the hydraulic fluid, ensuring precise and smooth operation of the system. The shearing blades are the primary cutting tools of the machine. There are two blades: the upper blade, which moves, and the lower blade, which remains fixed. Both blades are made from high-strength materials such as hardened steel to withstand the stress of cutting. The blades must be sharp and correctly aligned to ensure clean, accurate cuts. The upper blade is typically mounted on a moving tool holder, while the lower blade is fixed in place. The control system regulates the machine's operations, allowing operators to set and adjust various cutting parameters. Modern hydraulic shearing machines often feature computerized control systems (CNC) that provide enhanced precision and ease of use. Key functions of the control system include: Adjusts the distance between the upper and lower blades to accommodate different material thicknesses. Alters the angle of the cut for specific applications. Controls the length of the blade movement. The control system ensures that the machine operates within the desired parameters, facilitating precise and efficient shearing. Safety is paramount in the operation of hydraulic shearing machines. These machines are equipped with several safety features to protect operators and prevent accidents: A protective fence located at the front of the machine to prevent access to the cutting area during operation. A hydraulic pressing plate that holds the material in place during cutting, preventing it from shifting and ensuring accurate cuts. Easily accessible buttons that allow operators to immediately halt the machine in case of an emergency. A system that prevents the machine from operating beyond its capacity, protecting both the machine and the operator. The pressing device, often a hydraulic pressing plate, is installed in front of the frame. It ensures that the metal sheet remains stationary during the shearing process, thereby improving the quality and geometric accuracy of the cut. The pressing device operates by hydraulically pressing down on the material just before the shearing blades engage. The back gauge mechanism is a crucial component that ensures precise positioning of the material before cutting. It includes features such as micromotion, a back gauge motor, a digital display, and a lifting mechanism for the tailgate. This mechanism allows operators to set the desired dimensions and ensures consistent, accurate cuts. This feature allows for the adjustment of the gap between the upper and lower blades, which is essential for achieving clean cuts on materials of varying thicknesses. It is typically controlled by hydraulic motors and involves two wedge systems that adjust the side clearance of the cutting edge. The electrical unit controls the power supply and manages the hydraulic system. It includes components such as the main power switch, circuit breakers, and control buttons. The electrical unit ensures that the machine operates according to the set parameters and provides a user-friendly interface for operators. A robust lubrication system ensures that the moving parts of the shearing machine operate smoothly, reducing wear and tear. Regular lubrication minimizes friction and heat generation, extending the machine's lifespan and maintaining optimal performance. A hydraulic shearing machine comprises two blades: a fixed lower blade and a movable upper blade. The hydraulic system drives the upper blade downward in a controlled manner to shear the material placed between the blades. This process is facilitated by the hydraulic fluid, which plays a critical role in the machine's operation. Hydraulic fluid is indispensable for the functioning of a hydraulic shearing machine, serving several key purposes: Maintaining the hydraulic fluid at appropriate levels and ensuring its purity is essential for the smooth and efficient operation of the machine. Hydraulic shearing machines are versatile and can perform various types of shearing operations: This is the most common type of shearing operation, where the material is cut along a straight line. It is widely used in metal fabrication for creating straight-edged components. In angle shearing, the blades are set at an angle to achieve beveled cuts or specific angles on the material. This type of operation is useful in applications requiring angular components. Precision shearing involves making highly accurate cuts with minimal tolerance. This type of operation is essential in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where precision is critical. Multiple shearing operations involve making several cuts in a single pass. This is achieved by adjusting the back gauge and control system to perform sequential cuts without repositioning the material manually. Hydraulic shearing machines come in various capacities: Modern hydraulic shearing machines have seen several advancements: Guillotine shears are among the most common hydraulic shearing machines, known for their precision and ability to handle thick materials. They are characterized by their straight, vertical cutting action, where the upper blade descends in a straight line to meet the fixed lower blade. Example: In the automotive industry, guillotine shears are used to cut metal sheets for car body panels, ensuring precise and clean edges. Swing beam shears, also known as swing beam guillotines, operate with a pivoting motion. In these machines, the upper blade is attached to a swing beam, moving in an arc to shear the material against the static lower blade. This design allows for a more compact machine structure, which is advantageous for workshops with limited space. Swing beam shears are typically used for medium-thickness materials and are valued for their simplicity, ease of maintenance, and lower initial investment costs compared to guillotine shears. Example: In HVAC industries, swing beam shears are commonly used to cut metal sheets for ductwork, ensuring precise dimensions and clean edges. Fixed rake angle shears maintain a constant cutting angle, predetermined based on the machine's design. These robust machines are capable of handling thicker materials with ease. Example: In shipbuilding, fixed rake angle shears are used to cut large steel plates required for constructing ship hulls. Variable rake shears bring an added level of versatility to the shearing process by allowing the operator to adjust the rake angle (the angle of the cutting blade, typically ranging from 0.5 to 2.5 degrees). This adjustability is crucial for optimizing the cutting action for different material types and thicknesses, improving cut quality and reducing material deformation. Variable rake shears are particularly beneficial in applications requiring precision and varied cutting angles, offering greater flexibility than fixed rake designs. Particularly useful for cutting thicker materials (1/2 inch and above). Example: In aerospace, variable rake angle shears are used to cut aluminum sheets for aircraft components, where precision and minimal material deformation are critical. NC hydraulic shears come with a numerical control system that allows for precise control over the cutting process. Operators can input specific dimensions and angles, making these machines ideal for repetitive and complex cutting tasks. Example: Electronics manufacturing uses NC hydraulic shears to cut metal sheets for enclosures and components, ensuring precise dimensions and clean cuts. CNC hydraulic shears integrate advanced computer systems to execute intricate cutting patterns with high accuracy. These machines are designed for high-volume production and complex designs, offering advanced automation and precision. Example: In automotive manufacturing, CNC hydraulic shears are used to cut complex shapes for car components, ensuring high precision and efficiency. Tandem hydraulic shears consist of multiple shearing units working together, making them suitable for cutting exceptionally long sheets or high-volume production. Example: In construction, tandem hydraulic shears are used to cut long metal sheets for building facades, ensuring consistent quality and efficiency. In the metal fabrication industry, hydraulic shearing machines are essential for cutting sheets, plates, and bars with high accuracy. For example, these machines are used to produce components for machinery, construction, and consumer goods. The precision of hydraulic shears ensures that metal parts meet stringent specifications, reducing material waste and enhancing overall product quality. The automotive sector relies heavily on hydraulic shearing machines for cutting metal sheets and panels used in car bodies, frames, and other critical components. For instance, hydraulic shearing machines are used to cut metal sheets for car doors and hoods. These machines provide the necessary precision and consistency to meet the industry's high safety and performance standards, contributing to the structural integrity and aesthetic appeal of vehicles. Similar to the automotive industry, the aerospace sector also demands high precision and material efficiency, particularly for lightweight components. In the aerospace industry, hydraulic shearing machines are used to cut lightweight and durable materials such as aluminum and titanium alloys. For example, hydraulic shearing machines are essential for cutting lightweight aluminum sheets used in aircraft fuselage panels. The high precision offered by these machines ensures optimal performance and fuel efficiency, which are critical factors in aerospace applications. Hydraulic shearing machines play a vital role in the construction industry by cutting and processing materials like reinforcing bars, steel plates, and other structural components. These materials are essential for building robust and reliable structures, from residential buildings to large infrastructure projects. The ability of hydraulic shears to handle various thicknesses and materials makes them ideal for diverse construction needs. In electronics manufacturing, hydraulic shearing machines are used to cut materials for components like circuits and enclosures. They are also utilized in the production of household appliances, such as refrigerators and air conditioners, where stainless steel plates are commonly cut to precise specifications. The machines' ability to deliver consistent, clean cuts ensures the high quality of these consumer products. Alligator shears, a type of hydraulic shearing machine characterized by their hinged, crocodile-like jaws, are extensively used in recycling centers to cut scrap metal into smaller, more manageable pieces. This process facilitates the efficient handling, smelting, or repurposing of scrap materials. Reducing the volume of scrap metal through hydraulic shearing helps streamline recycling operations and promotes environmental sustainability. The agricultural sector also benefits from hydraulic shearing machines, which are used to produce metal components for equipment such as harvesters and tractors. The precision and efficiency of hydraulic shears ensure that these components meet the rigorous demands of agricultural operations, contributing to the durability and functionality of farm machinery. Hydraulic shearing machines are employed in the production of metal components for furniture and decorative items. The machines' ability to cut and shape metal sheets with precision allows for the creation of aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound products. This application is particularly important for custom furniture and high-end decorative items where design and quality are paramount. Yes, hydraulic shearing machines are capable of precision cutting, particularly when equipped with advanced control systems such as CNC or NC. These systems allow for high accuracy and repeatability, making them ideal for applications requiring precise dimensions and clean edges. Features like adjustable blade gaps and cutting angles further enhance the machine's precision capabilities. The lifespan of a hydraulic shearing machine varies based on factors such as usage, maintenance, and operating conditions. With proper care and regular maintenance, these machines can last several decades. Key components like blades and hydraulic systems may require periodic replacement, but the machine's robust construction ensures long-term reliability. Yes, several alternative machines can perform similar cutting tasks, including: Each alternative has its advantages and specific applications, so the choice depends on the material, precision requirements, and production volume. 45 Screw Extruder ,Twin Screw Small Extruder,30 Screw Extruder,35 Screw Extruder,25 Screw Extruder Dongguan Zhenggong Electromechanical Equipment Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.mixer-cn.comI. Introduction
What is a Hydraulic Shearing Machine
Brief History of Hydraulic Shearing Machines
Overview and Importance
II. Components of a Hydraulic Shearing Machine
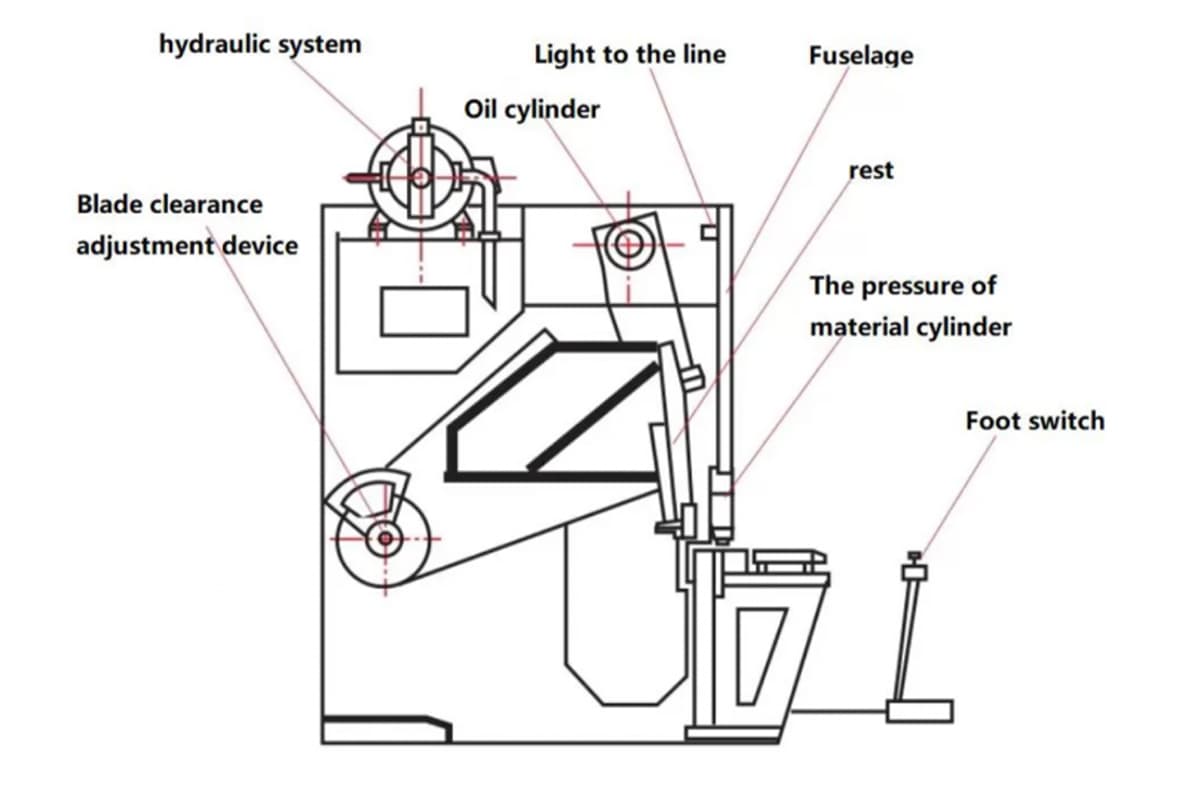
Frame
Hydraulic System
Hydraulic Pump
Hydraulic Fluid
Hydraulic Cylinders
Valves and Lines
Shearing Blades
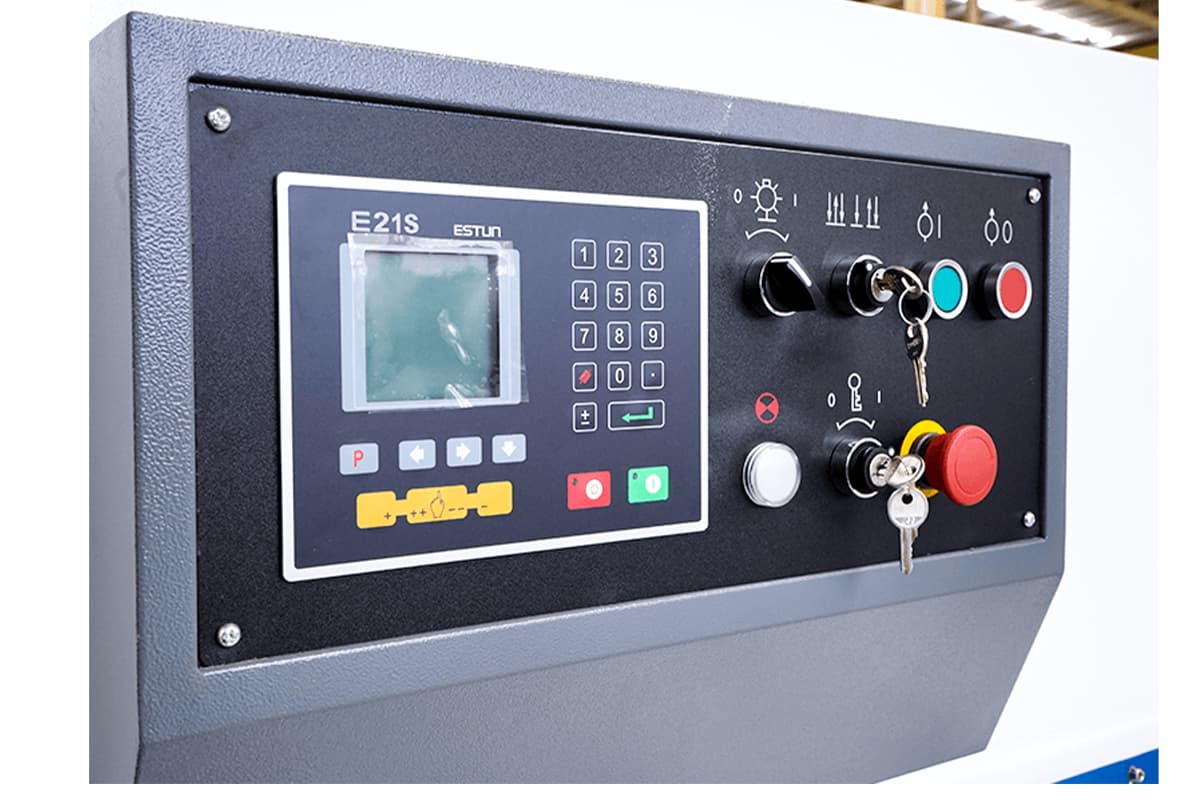
Control System

Blade Gap Adjustment
Cutting Angle Adjustment
Stroke Length Adjustment
Safety Features
Safety Guard
Pressing Device
Emergency Stop Buttons
Overload Protection
Pressing Device
Back Gauge Mechanism
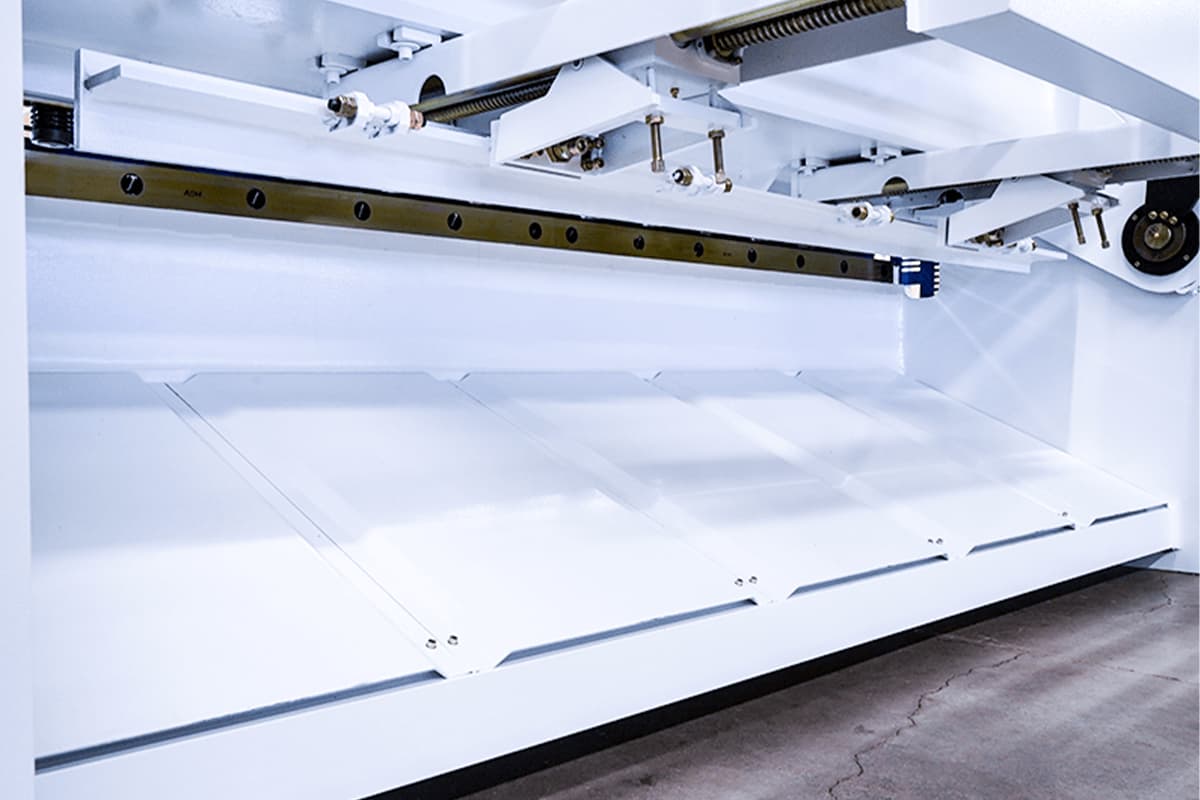

Shearing Edge Side Clearance Adjustment
Electrical Unit
Lubrication System
III. How Does a Hydraulic Shearing Machine Work?
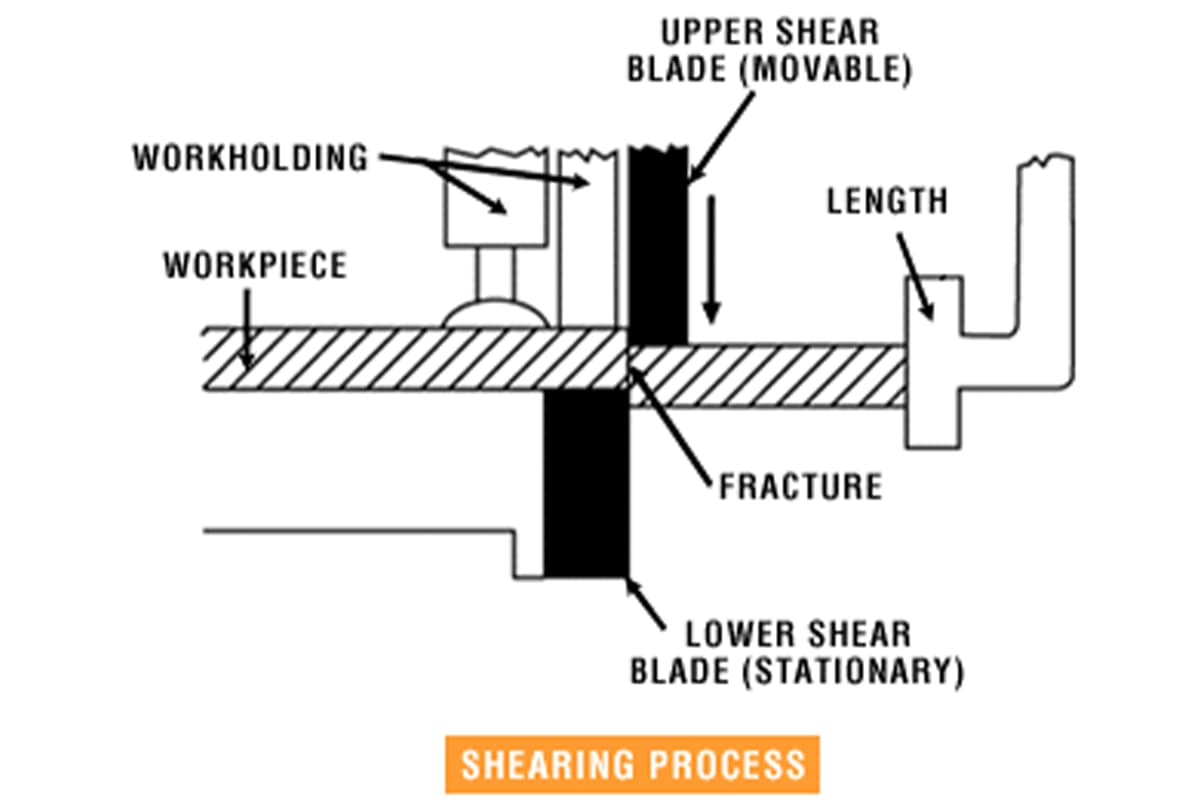
Basic Working Principle
Role of Hydraulic Fluid
Step-by-Step Process of Shearing
Types of Shearing Operations
Straight Line Shearing
Angle Shearing
Precision Shearing
Multiple Shearing
Capacity Ranges for Different Types
Recent Advancements
IV. Types of Hydraulic Shearing Machines

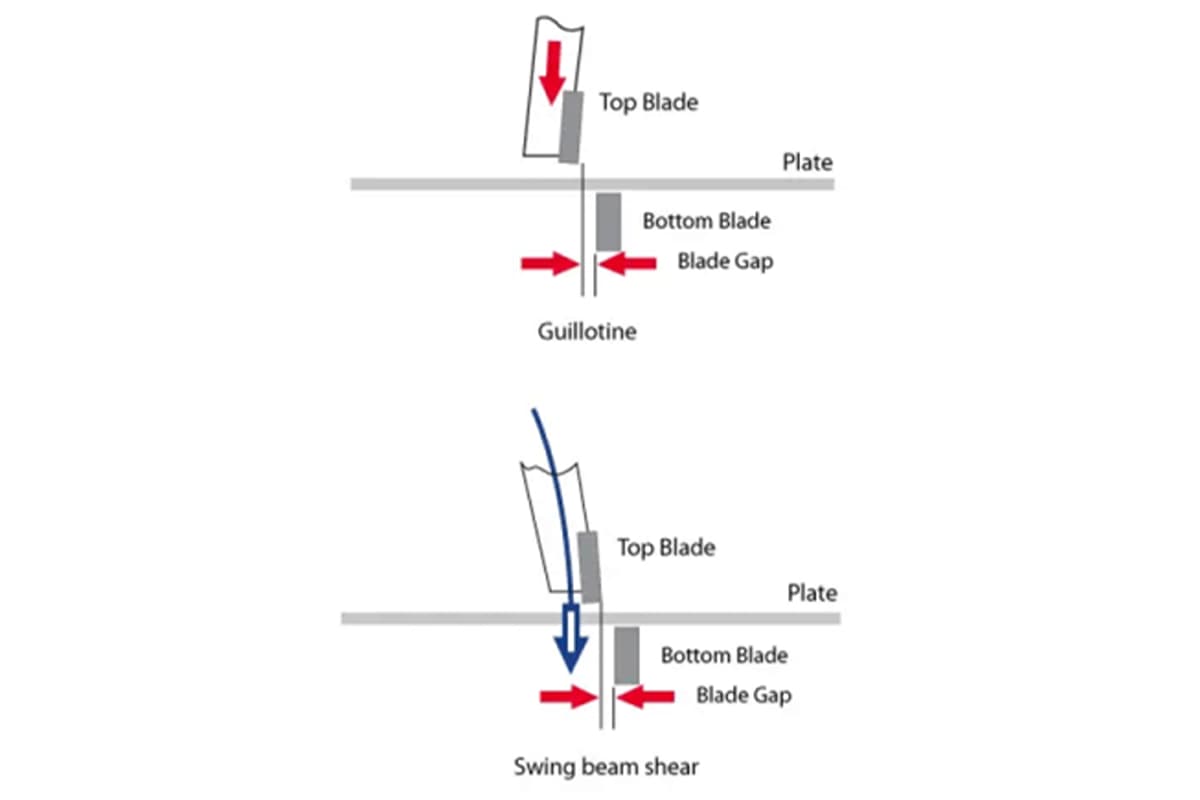
Guillotine Shears
Key Features:
Applications:
Swing Beam Shears
Key Features:
Applications:
Fixed Rake Angle Shears
Key Features:
Applications:
Variable Rake Angle Shears
Key Features:
Applications:
NC (Numerical Control) Hydraulic Shears
Key Features:
Applications:
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) Hydraulic Shears

Key Features:
Applications:
Tandem Hydraulic Shears
Key Features:
Applications:
Type Precision Versatility Power Requirements Material Thickness Range Production Volume Fixed Rake Angle High Low Moderate Narrow High Variable Rake Angle High High Moderate to High Wide Moderate to High NC/CNC Very High High Moderate to High Wide High Swing Beam Moderate Moderate Low to Moderate Thin to Medium Low to Moderate Guillotine High Moderate High Medium to Thick Moderate to High Tandem High Low Very High Medium to Thick Very High V. Common Applications of Hydraulic Shearing Machines

Metal Fabrication and Manufacturing
Automotive Industry
Aerospace Industry
Construction and Building
Electronics and Household Appliances
Recycling Industry
Agricultural Machinery
Furniture and Decorative Industries
VI. Frequently Asked Questions

1. Can hydraulic shearing machines be used for precision cutting?
2. What is the lifespan of a typical hydraulic shearing machine?
3. Are there any alternative machines to hydraulic shearing for similar applications?